
What Is Cellulose Fiber?
Cellulose fiber is a natural, plant-based fiber derived from the cellulose found in the cell walls of plants. It is one of the most abundant organic compounds on Earth and is commonly extracted from wood, cotton, or other plant materials. These fibers are highly versatile and biodegradable, making them eco-friendly and sustainable alternatives to synthetic fibers. Cellulose fibers are often used in textiles, paper products, and even in industrial applications like construction due to their strength, durability, and moisture-wicking properties. They also offer comfort, breathability, and resistance to wear and tear, making them an essential material in a wide range of industries.
Types of Cellulose Fibers
Cellulose fibers are divided into two main categories: natural cellulosic fibers and regenerated cellulosic fibers. The key difference lies in their processing—natural fibers are used in their raw plant-based form, while regenerated fibers are chemically processed to create new textile materials.
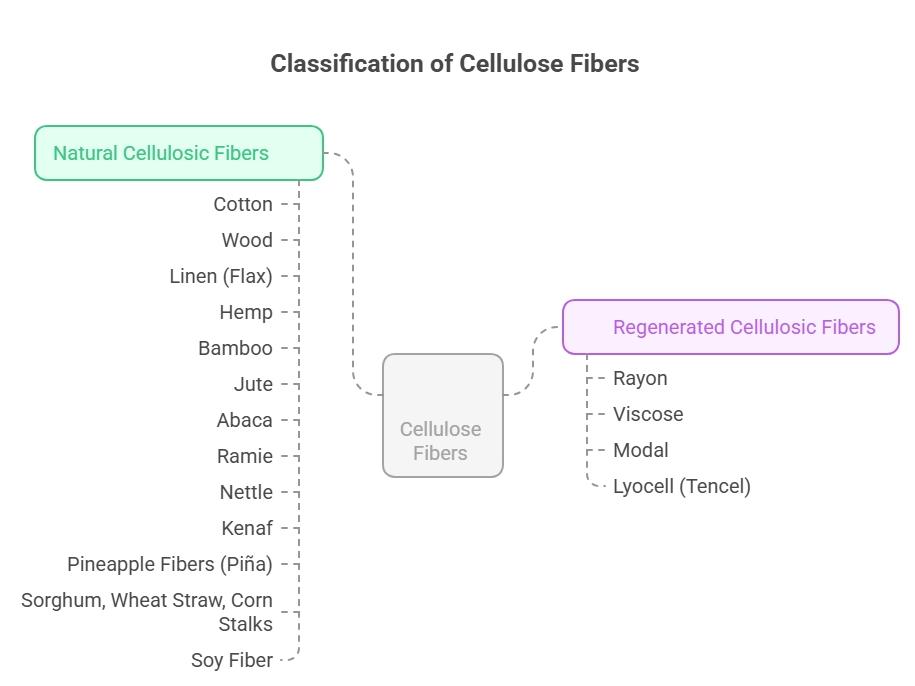
1. Natural Cellulosic Fibers
These fibers are obtained directly from plants with minimal chemical treatment. They are known for their renewability, biodegradability, and comfort, making them widely used in textiles, industrial products, and eco-friendly materials.
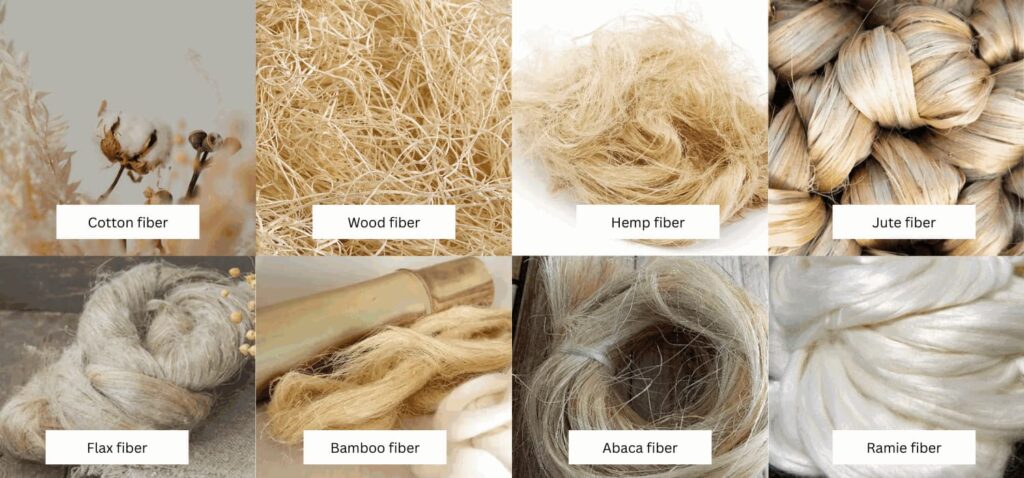
- Cotton – A soft, breathable fiber with excellent absorbency and comfort, making it one of the most widely used textiles worldwide. It is ideal for garments, bedding, towels, and medical supplies due to its hypoallergenic and skin-friendly properties.
- Wood – It is primarily used in the production of paper, cardboard, and other wood-based products. Wood fibers are valued for their strength, durability, and sustainability, making them an essential material in both industrial and environmental applications.
- Linen (Flax) – Made from flax plant stems, linen is strong, durable, and highly absorbent, offering a cool and fresh feel. It is commonly used for summer apparel, tablecloths, and bedding, and is valued for its elegant texture and natural luster.
- Hemp – A highly durable fiber with natural antibacterial properties, hemp is used for clothing, ropes, paper, and eco-friendly composites. It is resistant to mold and UV rays, and becomes softer with each wash while maintaining its strength.
- Bamboo – Naturally soft and smooth, bamboo fibers are processed for textiles that are breathable, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly. Bamboo is popular in towels, undergarments, and bedding due to its antibacterial properties and sustainable cultivation.
- Jute – A coarse and strong fiber, jute is widely used for making burlap sacks, twine, and eco-friendly packaging. Its rough texture makes it unsuitable for apparel but perfect for industrial and agricultural applications.
- Abaca – Extracted from banana plant species, abaca is highly durable and resistant to saltwater, making it suitable for ropes, ship lines, specialty papers, and tea bags. Its strength and flexibility are key reasons for its industrial importance.
- Ramie – A lustrous, silky fiber known for its resistance to bacteria and mildew. It is used in upholstery, textiles, ropes, and decorative fabrics. Ramie blends well with other fibers, enhancing durability and sheen.
- Nettle – Traditionally used for textiles, nettle fibers are strong, breathable, and sustainable. They have a silky appearance and are making a comeback in eco-conscious fashion for their low environmental impact and durability.
- Kenaf – Derived from a hibiscus plant, kenaf fibers are strong and resilient. They are primarily used for paper production, packaging materials, and composites in building industries due to their strength and fast-growing nature.
- Pineapple Fibers (Piña) – Soft and lightweight fibers extracted from pineapple leaves, used in fine garments, barong tagalog, and accessories. Piña fabric is known for its delicate sheen, breathability, and biodegradability.
- Sorghum, Wheat Straw, Corn Stalks – Agricultural byproduct fibers used mainly for paper, composites, and building materials. They offer a low-cost, sustainable solution for industrial applications and help reduce agricultural waste.
- Soy Fiber – Made from soybean protein residue, soy fibers are soft, silky, and biodegradable. Often referred to as “vegetable cashmere,” they are used in high-end textiles, blending comfort with eco-friendly innovation.

2. Regenerated Cellulosic Fibers
These fibers are man-made but derived from natural plant cellulose. They combine the comfort of natural fibers with enhanced strength, versatility, and uniformity due to controlled processing methods.
- Rayon – A versatile, semi-synthetic fiber that mimics silk in softness and drape. It absorbs moisture well, making it comfortable for clothing, but it can wrinkle easily and requires gentle care.
- Viscose – Known for its silky feel and bright colors, viscose is affordable and widely used in fashion textiles, linings, and household fabrics. While soft and absorbent, it is less durable than other regenerated fibers.
- Modal – A refined type of rayon, modal is soft, smooth, and resistant to shrinkage. It is commonly used in underwear, sportswear, and bed linens due to its luxurious texture and excellent moisture management.
- Lyocell (Tencel) – Produced using an eco-friendly, closed-loop process, lyocell is strong, breathable, and wrinkle-resistant. It is widely used in activewear, bedding, and eco-conscious fashion for its silky touch and sustainable production.

Benefits of Using Cellulose Fiber in Concrete
Superior Crack Control
Cellulose fibers are excellent at preventing cracks in concrete and asphalt. By adding these fibers to your mix, you reduce the risk of plastic shrinkage cracks, ensuring a stronger, more durable surface. The fibers help maintain the integrity of the material, even during the drying process.
Improved Workability & Cohesion
These fibers enhance the workability of your mix, making it easier to handle and apply. They also improve the cohesion of the mix, allowing for better bonding between materials. This results in a smoother, more uniform finish in your concrete or asphalt projects.
Eco-Friendly & Non-Toxic
Cellulose fibers are made from natural plant materials, making them an eco-friendly option for construction. They’re non-toxic, ensuring a safer working environment and a reduced environmental footprint compared to synthetic fibers.
Enhanced Water Retention & Controlled Evaporation
Cellulose fibers help retain moisture in the mix, which is crucial for hydration and proper curing. This control over evaporation ensures that your materials set correctly and maintain their strength, especially in hot or windy conditions.
[Related post: Why use polypropylene fiber in concrete?]
What Is Cellulose Fiber Used For?
Cellulose fiber is a versatile material with a wide range of applications across various industries. Its natural properties, such as strength, absorbency, and biodegradability, make it an ideal choice for numerous uses.
Construction
In construction, cellulose fiber is commonly used as a reinforcement material in concrete and asphalt. It enhances crack resistance, improves workability, and ensures better water retention. This makes it essential for creating durable pavements, roads, and structural elements.
Textile Industry
In textiles, cellulose fibers are used to make fabrics like cotton, linen, and rayon. These fibers are valued for their breathability, softness, and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for clothing and upholstery.
Paper Manufacturing
Cellulose is the main component of paper, and cellulose fibers are crucial in paper production. They contribute to the strength, texture, and flexibility of the paper, making them essential in everything from printing to packaging materials.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, cellulose fibers are often used as excipients in tablet production. They act as binders, ensuring that the active ingredients in medications are properly formed and stable.
Environmental Applications
Due to its biodegradability, cellulose fiber is used in eco-friendly products like biodegradable packaging and cleaning materials. It’s also used in filtration systems, as it can efficiently filter out particles in water and air.
[Related post: Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete]
Applications of Cellulose Fiber in Construction
Cellulose fiber is widely used in construction due to its strength, durability, and eco-friendly properties. When added to concrete and asphalt mixes, it enhances performance in various construction projects, from roadways to industrial flooring.
Road Construction
Cellulose fibers are added to asphalt in road construction to improve the crack resistance and durability of the pavement. The fibers help prevent plastic shrinkage cracks during the curing process, resulting in smoother, longer-lasting roads. They also improve the flexibility and load-bearing capacity of the pavement, making it more resilient to wear and tear from traffic and weather conditions.
Airport Runways
In airport runway construction, cellulose fibers are used to reinforce the concrete, ensuring a strong and stable surface that can withstand heavy aircraft landings. The fibers provide excellent crack control and reduce the risk of surface degradation, enhancing the safety and longevity of runways.
Industrial Flooring
Cellulose fibers are commonly incorporated into industrial flooring systems, especially in areas with high traffic or heavy machinery. They improve the workability and cohesion of the flooring mix, ensuring a smooth finish while increasing resistance to cracking and surface wear. This makes cellulose fibers ideal for warehouses, factories, and commercial spaces.
Precast Concrete Products
For precast concrete elements like pipes, panels, and barriers, cellulose fibers help improve the overall strength and durability of the products. The fibers reduce shrinkage and enhance the bonding between the concrete components, ensuring that the precast products can withstand the rigors of transportation, installation, and long-term use.
Conclusion
Cellulose fiber stands out as a sustainable and versatile material with broad applications across multiple industries. From its natural origins in plants to its processed forms like rayon and lyocell, cellulose fibers offer a range of benefits, including durability, comfort, and eco-friendliness. Whether in the textile industry, construction, or environmental solutions, this natural fiber plays a vital role in creating products that are both functional and sustainable. By continuing to innovate and integrate cellulose fibers into everyday products, we can further promote a more eco-conscious future.
Related Products

Cellulose Fiber 2mm
Cellulose Fiber 2mm is a premium wood-based fiber designed to reinforce concrete, improving tensile strength, reducing cracks, and enhancing durability.

Cellulose Fibers 3mm
It is a natural, high-performance fiber for concrete reinforcement. Derived from premium wood, it enhances tensile strength, reduces shrinkage cracks, and improves concrete durability.
Related Articles


Differences Between Plasticizer and Superplasticizer: A Complete Guide for Beginners

Finding the Right Consistency of Tile Adhesive: The Key to Strong and Lasting Tiles

Fiber Reinforced Concrete vs Rebar: Which Is Best for Your Project?

What Is Cellulose Fiber? Types, Benefits & Applications in Industry


