Status 1: Force majeure across the world
Due to the global spread of the epidemic in 2020, factories worldwide have been collectively closed. Although the outbreak in some countries has been brought under control in mid-2020, the decline in global productivity has not yet fully recovered.
In early 2021, affected by the cold polar current, parts of the southern Texas state began to experience extreme weather such as snowfall, ice, and freezing rain on the night of February 14, causing road icing and road closures. Sub-zero conditions have destroyed most of Texas’ electrical grid, leaving millions of people without heat or electricity, especially in and around Houston and Austin.
Texas is an important center of American energy, and Houston even has “energy capital”. There are a large number of petroleum and chemical facilities in and around the state. The power outage has “paralyzed” the production of many oil refining and chemical plants in the state. ICIS pointed out that the petrochemical industry in the Gulf of Mexico has been severely affected so far. So far, ICIS has confirmed the closure of more than 50 petrochemical plants.
Dow announced force majeure on its factories in Texas, Louisiana, and Kentucky on February 18:
Dow Chemical stated that the current situation is dire. Due to extreme weather conditions, the operating temperatures of Dowsder Park, St Charles, Texas City, Freeport, Bayport, and Louisville are below freezing, resulting in involuntary planned shutdowns, inability to load products, or extended downtime.
BASF announced on February 17, 2021: From February 14 to 16, 2021, Louisiana and Texas, including the Geismar and Los Angeles areas, experienced prolonged periods of severe weather and freezing temperatures. The factory’s Geismar manufacturing base operating at BASF has been affected due to the severe interruption of key raw materials and subsequent freezing and damage to BASF’s facilities.
Celanese declared force majeure against various chemical substances, including VAM and acetic acid, on February 18. The company said it had to cut production due to a lack of natural gas, electricity, drinking water and fire-fighting water, and other raw materials needed to operate the plant.
Status 2: Global imbalance between supply and demand
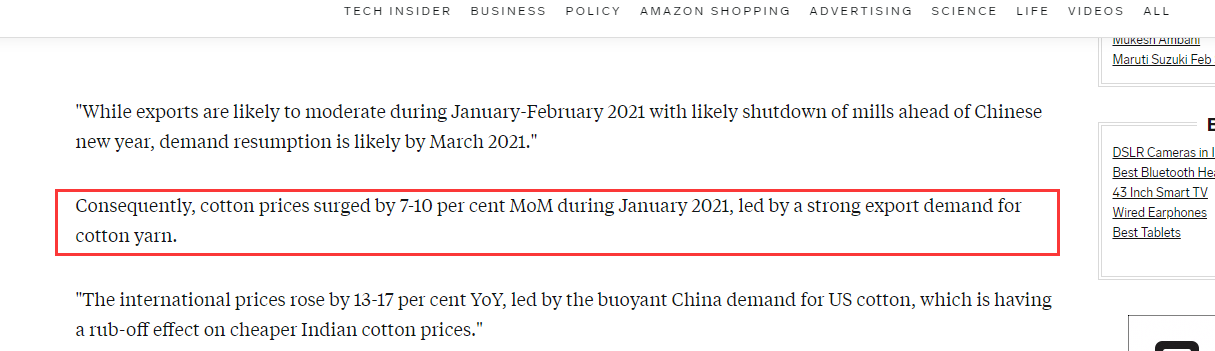
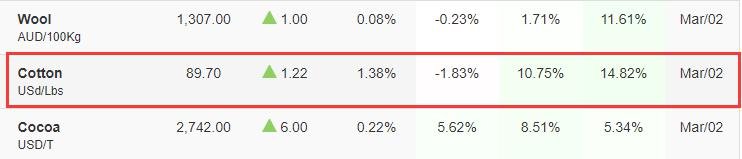
As the epidemic eased at the beginning of 2021, demand for raw materials for production began to recover. At this time, a once-in-a-hundred-year snowstorm in the United States paralyzed many large chemical plants and terminated the supply chain of chemical raw materials. China has become a major supplier of many chemical raw materials. In 2021, China’s chemical raw material exports have surged, and the shortage of supply in the market has caused the price of raw materials for Chinese factories to rise.
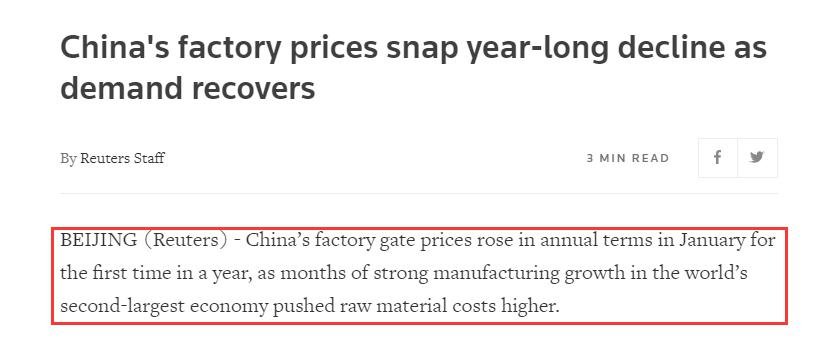
In this article, Reuters analyzed the January PPI (Producer Price Index) and pointed out that strong manufacturing growth in the world’s second-largest economy pushed raw material costs higher, causing China’s factory gate prices too rose in an annual term in January for the first time in a year.
MIKEM Announces Price Increase
From what we have discussed above, we believe you can understand that we have experienced significant cost growth since 2020. And the cost growth will last for a long time. We have made every effort to control and absorb the increases over the past 6 months. It is no longer possible for us to fully absorb the effects because of the increasing raw material prices and the decreasing exchange rate between USD and CNY.
We have no other choice but to increase the prices of products and solutions. Our focus remains on delivering value to and serving our customers across the world. MIKEM is committed to long-standing relationships including consistent supply and product innovation; therefore, it is necessary to implement a price increase. The changes will be effective on all orders shipped on or after 5th, March 2021.